Redistributing Static Routes. Router (config)#ip route 10.1.1.0 255.255.255.0 serial 0/0/0. Creates a static route for network 10.1.1.0/24 exiting out of interface Serial 0/0/0. Router (config)#router eigrp 10. Starts the EIGRP routing process. Router (config-router)#redistribute static. To reinforce the earlier statement that the seed metric for routes redistributed into EIGRP is infinity, we’ll initially not configure any metrics and let the seed metrics take effect. The redistribute command was issued under router configuration mode for each routing protocol, and no metric was specified. Now let’s deal with redistribution. To do redistribution from another routing protocol into EIGRP you have to use redistribute command as a router eigrp subcommand. Further there are several options: protocol from which to take routes, it could be Connected, Static, OSPF, EIGRP, ISIS, BGP, RIP. Static redistribution is the same process for any dynamic routing protocol and all dynamic routing protocols rather it be RIP, EIGRP or OSPF, all use the same commands to redistribute the static routes into the routing process. To configure static redistribution you’ll use the redistribute static metric metric# whereas the metric is a statically configured metric which is assigned to the redistributed route(s). Static routesand connected interfacescan be redistributed into a routing protocol as well. Routes will only be redistributed if they exist in the routing table. Routes that are simply in a topology database (for example, an EIGRP Feasible Successor), will neverbe redistributed.

This chapter provides information about the following redistribution topics:
- Defining seed and default metrics
- Redistributing connected networks
- Redistributing static routes
- Redistributing subnets into OSPF
- Assigning E1 or E2 routes in OSPF
- Redistributing OSPF internal and external routes
- Configuration example: route redistribution for IPv4
- Configuration example: route redistribution for IPv6
- Verifying route redistribution
Route filtering using the distribute-list command
- Configuration example: inbound and outbound distribute list route filters
- Configuration example: controlling redistribution with outbound distribute lists
- Verifying route filters
Route filtering using prefix lists
- Configuration example: using a distribute list that references a prefix list to control redistribution
- Verifying prefix lists
Using route maps with route redistribution
- Configuration example: route maps
- Manipulating redistribution using route tagging
- Changing administrative distance for internal and external routes
- Passive interfaces
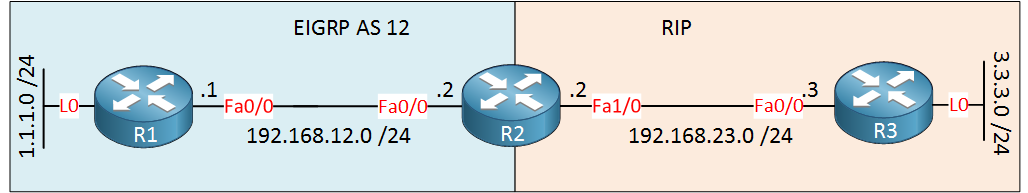
Command To Redistribute Static Route In Eigrp
Defining Seed and Default Metrics
Redistribute Static Command
Router(config)#router eigrp 100 | Starts the EIGRP routing process. |
Router(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0 | Specifies which network to advertise in EIGRP. |
Router(config-router)#redistribute rip | Redistributes routes learned from RIP into EIGRP. |
Router(config-router)#default-metric 1000 100 250 1 1500 Or | The metrics assigned to these learned routes will be calculated using the following components: |
Router(config-router)#redistribute rip metric 1000 100 250 1 1500 | 1000 = Bandwidth in Kbps |
100 = Delay in tens of microseconds | |
255 = Reliability out of 255 | |
1 = Load out of 255 | |
1500 = Maximum transmission unit (MTU) size | |
The metric keyword in the second option assigns a starting EIGRP metric that is calculated using the following components: 1000, 100, 255, 1 1500. |
